 |
| A water bear, known as the strongest animal on Earth, is holding on to moss. Water bears can withstand extreme environments and are frequently used in recent space experiments. Photo Eye of Science |
There are animals that can survive extreme cold temperatures of -273 degrees Celsius or temperatures as high as 151 degrees, which is enough to boil water. It is a water bear, an arthropod whose body length does not exceed 1.5 mm. Scientists have discovered the secret to water bears surviving in space. Cell time is much slower than others. It was confirmed through experiments that human aging can be suppressed using the same principle.
Earth's mightiest animals are opening new paths to overcoming human diseases and suppressing aging. Biopharmaceuticals made from human proteins can also be stored for a long time at room temperature without a refrigerator by using water bear protein. This means that water bears can bring medical benefits to underdeveloped countries that lack social infrastructure.
Granting water bear extreme viability to human cells
An international collaborative research team led by Thomas Boothby, a professor of molecular biology at the University of Wyoming, recently published in the international journal 'Protein Science', "We discovered that water bear proteins can slow down the molecular processes of human cells." Researchers at the University of Bristol in the UK, the University of Washington and the University of California at Merced in the US, the University of Bologna in Italy, and the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands also participated in this study.
Water bears move on eight legs and live by catching plankton in moss. Its name is tardigrade, which means 'animal that walks slowly', but its nickname, water bear, is more famous because it looks like a bear swimming in the water. Water bears can live without water and food for over 30 years. It can withstand not only extremely low temperatures and high heat, but also water pressure six times higher than that of the Mariana Trench, the deepest place on Earth.
Especially in space, there are no problems. Most animals die from a radiation dose of about 10 to 20 Gy (gray), but water bears can withstand a whopping 5,700 Gy. In 2007, they went into space on an unmanned spacecraft of the European Space Agency (ESA) and returned to Earth 12 days later. Some of them survived when they were provided with moisture. A water bear was also carried on the unmanned spacecraft that Israel sent to the moon in 2019.
Researchers at the University of Wyoming noted that when water bears encounter extreme environments, they curl their bodies into a ball and fall into a state of suspended animation. According to the results of this study, in extreme environments, water bears' cells turn into a gel-like state, their metabolism slows down, and they enter a state of suspended animation called biological quiescence.
Scientists explained that water bears survive in extreme environments because a sugar called trehalose protects key biological substances such as proteins. Trehalose protects what little moisture is left in the body when there is no water. Thanks to this, even if the temperature suddenly rises, the moisture does not expand and does not destroy the cells. It also prevents moisture from freezing and tearing cells.
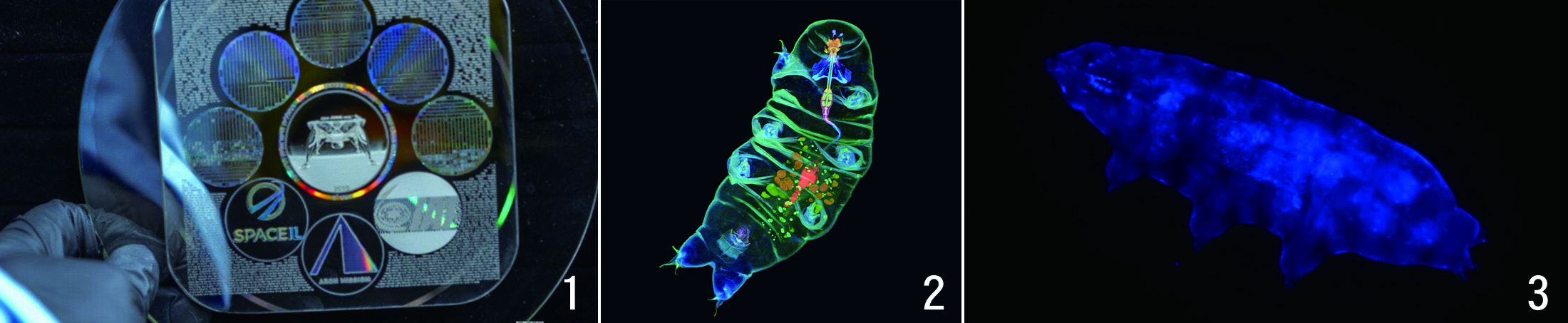 |
| 1 A data storage device containing 30 million pages of human records loaded on the Israeli lunar probe Beresheet in 2019. We also sent thousands of water bears to its surface. Photo by Arch Mission Foundation 2 Turged DeCarvallo's 'Water Bear' won first place in the U.S. at the 2020 Olympus Microscope Photo Exhibition. Various fluorescent dyes were injected and pictures were taken under a microscope. Photo Olympus 3 A water bear glows blue when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays. Fluorescent pigments in the skin change deadly ultraviolet rays into harmless blue light. Photo Indian Institute of Science |
But that wasn't all. The researchers found that trehalose protects biological materials sensitive to stress, while a protein called 'CAHS D' slows metabolism. Professor Boothby demonstrated through experiments that the extreme survival ability of water bears can be introduced to humans. The water bear CAHS D protein, which induces apnea, was injected into human kidney cells. Then, like water bears, human cells were able to overcome environmental stress by forming a gel and slowing down their metabolism.
The important thing is that this entire process is reversible. When the stressor disappeared, the water bear's gel dissolved and the human cell's metabolism returned to normal. This means that water bear protein can be used only under certain conditions, and can be restored to its original state when the environment improves.
Groundbreaking advancements in protein medicine and cell storage
Professor Boothby said, “The results of this study suggest a way to slow aging and improve storage and stability by inducing a state of suspended animation in cells and the entire living body.” If human cells can overcome environmental stress, aging is delayed. In theory, as shown in the movie, terminally ill patients could remain in suspended animation and then wake up and receive treatment in a future where medical science has advanced.
In reality, it could bring about great progress in the storage of biopharmaceuticals made from human proteins. In fact, in 2023, researchers demonstrated that hemophilia treatment protein can be stored without refrigeration using water bear protein. Hemophilia is a disease in which bleeding does not stop due to a genetic deficiency of blood clotting factors.
Human coagulation factor VIII treats bleeding in patients with hemophilia. The problem is that blood clotting factor VIII is inherently unstable. If it is not refrigerated at the appropriate temperature, it will decompose immediately. It is useless in places where there is no refrigerated storage infrastructure, such as disaster sites or underdeveloped countries.
Researchers at the University of Wyoming announced in 2022 that trehalose sugar and CAHS D protein have a synergistic effect in protecting the biological material of water bears in waterless environments. In 2023, researchers stabilized blood coagulation factor VIII by controlling two substances. The researchers predicted, “If treated with CAHS D protein, hemophilia treatment can be dried and stored for a long time without a refrigerator,” and added, “The same method can be applied to other biopharmaceuticals such as vaccines, antibodies, stem cells, and blood products.”
Block UV rays with a fluorescent dye shield.
Scientists have revealed one after another how water bears became the most powerful animals on Earth. A research team led by Dr. Sandeep Es-warappa of the Indian Institute of Science wrote in the international academic journal 'Biology Letters' published by the Royal Society in 2020, "Water bears use fluorescent pigment as a shield to survive exposure to lethal ultraviolet (UV) rays. “You can survive,” he said.
The research team accidentally did not turn off the ultraviolet sterilizing lamp, but some water bears did not die even after being exposed to ultraviolet rays. Bacteria and nematodes died within 5 minutes, and all other water bears died within 15 minutes. However, all red-brown water bears survived despite being exposed to the same amount of ultraviolet rays. Unusually, this water bear glowed blue when exposed to ultraviolet light. The researchers explained that fluorescent pigments in the water bear's skin change deadly ultraviolet rays into harmless blue light.
In 2016, a research team led by Professor Kunieda Takekazu of the University of Tokyo announced in the international academic journal 'Nature Communication' that they had discovered a 'shield' protein that protects the DNA of water bears in extreme environments. The research team completely decoded the water bear's DNA and discovered a protective protein called 'Dsup'. When exposed to radiation, this protein hugs and protects DNA.
It worked for people too. When the gene that creates the Dsup protein was inserted into human kidney cells, cell damage caused by radiation was reduced to half of the normal level. Professor Kunieda said, “In the future, it could help protect the human body during space travel, radiation treatment, and work in radiation-contaminated areas.” Water bears have more genes that prevent or repair DNA damage than other animals. Astronauts going into deep space in the distant future may be armed with water bear proteins and genes.
No comments:
Post a Comment